Read / Write Vehicle ECU on Bench or OBD or on Boot Mode?
Comparing ECU reading and writing methods, there are three primary options: OBD, Bench, and Boot mode.
Read / Write ECU via OBD vs on Bench vs in boot mode
Comparing ECU reading and writing methods, there are three primary options: OBD, Bench, and Boot mode.
OBD Read / Write:
OBD reading and writing is a widely adopted and effective method for vehicle tuning. It has significantly transformed the industry by making tuning accessible to a broader audience. OBD, which stands for "on-board diagnostic port," provides direct access to the vehicle's ECU. Typically located beneath the steering wheel or around the glove box, this port enables mechanics to quickly diagnose faults by scanning the engine control unit for error codes. While some vehicles allow full data reads via OBD, others may only permit partial reads. In certain newer car models, the software is locked, but specific tools offer VR files stored on servers (
ECUhelp 3.0 offer free VR files). These files match the ECU's software version, allowing the tool to bypass tuning protection and write modified files. However, it is essential to consider battery strength during OBD tuning to avoid communication interruptions that could lead to critical errors.

Image 1:
ecuhelp kt200 program ecu (unlock pcr2.1) via OBD.
Bench Read / Write:
Working on the bench refers to the process of removing the ECU from the vehicle and connecting it directly to the pins that the car's wiring harness would typically plug into. To perform this method, you need an external power source and a boot cable. Power is connected to multiple pins, including ground, as well as other communication interfaces like CAN+ and CAN- or KLine. This approach is also known as working in service mode and is commonly used by manufacturers such as Bosch. In this mode, you can typically read the entire memory storage of the ECU. It provides a comprehensive and direct method for accessing and manipulating the ECU's data and settings.
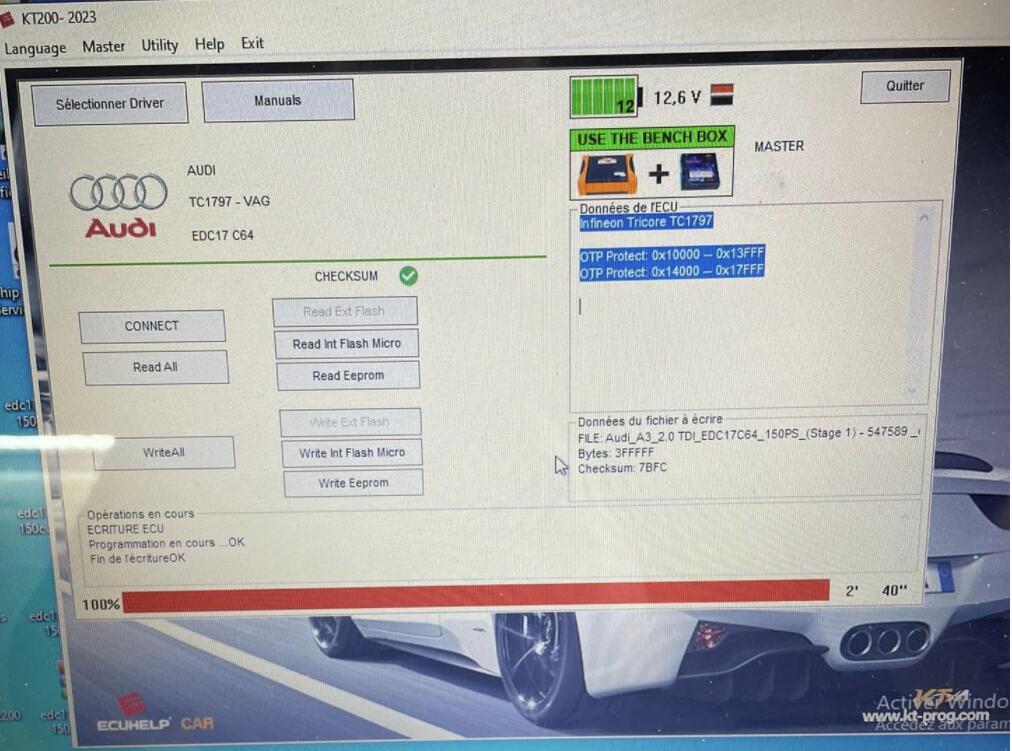
Image 2: ECUHELP KT200 program ECU (EDC17 C64) on Bench
Boot Read / Write:
Boot reading and writing is another method performed on bench, and it is considered the most technical-looking approach as it involves opening the ECU and directly connecting pins to the chipboard. The basic principles are similar to working in service mode, where you connect to the connection pins. However, in boot mode, you connect boot or earth pins directly to the board to bypass the security chip. This enables you to access and modify the full memory, effectively bypassing the TRICORE protection commonly found in a wide range of Bosch (M)EDC17 ECUs. Boot mode is often the initial option available when a new hardware solution is developed, as it allows developers to explore all the protocols and blocks within the ECU. It provides advanced access to the ECU's internal components and settings, facilitating comprehensive modifications and enhancements.

Image 3. ECUHELP KT200 program ECU on Boot
What is the optimal method for extracting maps from a vehicle? The answer to this question depends on various factors such as the specific situation, available tools, and required software solution. Each method has its advantages and specific applications in the market. OBD reading is often considered the simplest and fastest approach, but it lacks the security and protection provided by bench reading. On the other hand, boot mode, although potentially less secure than bench mode, offers the ability to bypass manufacturer deterrents, making it a valuable asset in a tuner's toolkit.


